GIẢI THÍCH THUẬT NGỮ,
NỘI DUNG VÀ
PHƯƠNG PHÁP TÍNH MỘT SỐ CHỈ TIÊU THỐNG KÊ
DÂN SỐ VÀ LAO ĐỘNG
DÂN SỐ
Dân số là tập hợp người sinh sống
trong một quốc gia, khu vực, vùng địa lư kinh tế
hoặc một đơn vị hành chính.
Trong
thống kê, dân số được thu thập theo khái niệm
nhân khẩu thực tế thường trú tại hộ,
là những người thực tế thường xuyên
ăn, ở tại hộ tính đến thời điểm
điều tra đă được 6 tháng trở lên, trẻ
em mới sinh trước thời điểm điều
tra và những người mới chuyển đến sẽ
ở ổn định tại hộ, không phân biệt có
hay không có hộ khẩu thường trú tại xă, phường,
thị trấn đang ở và những người tạm
vắng. Nhân khẩu thực tế thường trú tại
hộ gồm:
-
Người thực tế thường xuyên ăn, ở tại
hộ tính đến thời điểm thống kê đă
được 6 tháng trở lên.
-
Người mới chuyển đến chưa được
6 tháng nhưng xác định sẽ ăn, ở ổn
định tại hộ và những trẻ em mới sinh
trước thời điểm thống kê; không phân biệt
họ đă có hay không có giấy tờ pháp lư chứng nhận
sự di chuyển đó.
-
Người tạm vắng gồm người rời hộ
đi làm ăn ở nơi khác chưa được 6
tháng tính đến thời điểm thống kê; người
đang làm việc hoặc học tập trong nước
trong thời hạn 6 tháng; người đang đi
thăm, đi chơi nhà người thân, đi nghỉ hè,
nghỉ lễ, đi du lịch, sẽ quay trở lại hộ;
người đi công tác, đi đánh bắt hải sản,
đi tàu viễn dương, đi buôn chuyến; người
được cơ quan có thẩm quyền cho phép đi
làm việc, công tác, học tập, chữa bệnh, du lịch
ở nước ngoài, tính đến thời điểm
thống kê họ vẫn c̣n ở nước ngoài trong thời
hạn được cấp phép; người đang chữa
bệnh nội trú tại các cơ sở y tế; người
đang bị ngành quân đội, công an tạm giữ.
Dân số trung bình
Dân
số trung bình là dân số tính bình quân cho
cả một thời kỳ.
Công
thức tính:
-
Nếu chỉ có số liệu tại hai thời
điểm (đầu và cuối của thời
kỳ ngắn, thường là một năm),
sử dụng công thức:
|
Ptb |
= |
P0 + P1 |
|
2 |
Trong
đó:
Ptb: Dân
số trung bình;
P0: Dân
số đầu kỳ;
P1: Dân
số cuối kỳ.
-
Nếu có số liệu tại nhiều thời
điểm cách đều nhau, sử dụng công thức:
|
|
|
P0 |
+ P1 |
+ .... |
+ Pn-1 + |
Pn |
|
2 |
2 |
|||||
|
n |
||||||
Trong
đó:
Ptb: Dân
số trung bình;
P0,1,...,n:
Dân số ở các thời điểm 0, 1,...,
n;
n: Số
thời điểm cách đều nhau.
-
Nếu có số liệu tại nhiều thời
điểm không cách đều nhau, sử dụng
công thức:
|
Ptb |
= |
Ptb1t1
+ Ptb2t2 + .... + Ptbntn |
|
∑ti |
Trong đó:
Ptb: Dân
số trung bình;
Ptb1: Dân
số trung bình của khoảng thời gian
thứ nhất;
Ptb2: Dân
số trung bình của khoảng thời gian
thứ 2;
Ptbn: Dân
số trung bình của khoảng thời gian
thứ n;
ti:
Độ dài của khoảng thời gian
thứ i.
Dân
số thành thị
là dân số của các đơn vị lănh thổ
được Nhà nước quy định là khu vực
thành thị (phường và thị trấn).
Dân
số nông thôn
là dân số của các đơn vị lănh thổ
được Nhà nước quy định là khu vực
nông thôn (xă).
Mật
độ dân số
là số dân tính bình quân trên một kilômét
vuông diện tích lãnh thổ.
Mật độ dân số
được tính bằng cách chia dân
số (dân số thời điểm hoặc dân số
trung b́nh) của một vùng dân cư nhất
định cho diện tích lănh thổ của vùng
đó.
Mật độ dân số
có thể tính cho toàn quốc hoặc riêng
từng vùng (nông thôn, thành thị, vùng kinh
tế - xă hội); từng tỉnh, từng
huyện, từng xã,... nhằm phản ánh
tình hình phân bố dân số theo địa lý
vào một thời gian nhất định.
Công
thức tính:
|
Mật độ dân số |
= |
Dân số |
|
Diện tích lănh thổ |
Số hộ
Hộ
là một đơn vị xă hội, bao gồm một
người ăn riêng, ở riêng hoặc nhiều
người ăn chung và ở chung. Đối
với những hộ có từ 2
người trở lên, các thành viên trong hộ
có thể có hay không có quỹ thu chi chung;
có thể có hoặc không có quan hệ huyết
thống, nuôi dưỡng hoặc hôn nhân; hoặc kết
hợp cả hai.
Tỷ số giới
tính của dân số phản ánh số
lượng nam giới tính trên 100 nữ giới.
Tỷ số giới tính của dân số
được xác định theo công thức sau:
|
Tỷ số giới tính
|
= |
Tổng số nam |
× 100 |
|
Tổng số nữ |
Tỷ
suất sinh thô
Tỷ
suất sinh thô cho biết cứ 1000 dân, có bao nhiêu
trẻ em sinh ra sống trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Công
thức tính:
|
CBR (‰) |
= |
B |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Trong
đó:
CBR: Tỷ suất
sinh thô;
B: Tổng số sinh trong thời kỳ
nghiên cứu (tổng số trẻ em sinh ra sống trong thời
kỳ nghiên cứu);
Ptb: Dân
số trung b́nh trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Tổng
tỷ suất sinh (TFR)
Tổng
tỷ suất sinh phản ánh số con đã sinh ra
sống tính bình quân trên một phụ nữ trong
suốt thời kỳ sinh đẻ nếu người
phụ nữ đó trải qua các tỷ suất sinh
đặc trưng của thời kỳ nghiên cứu
đã cho trong suốt thời kỳ sinh đẻ.
Công thức tính theo từng độ
tuổi:
![]()
Trong
đó:
TFR: Tổng tỷ
suất sinh (số con/phụ nữ);
Bx: Số trẻ sinh ra sống trong thời
kỳ nghiên cứu của những bà mẹ (x) tuổi;
x: Khoảng tuổi
01 năm;
Wx: Số
phụ nữ (x) tuổi có đến thời
điểm nghiên cứu.
Các tỷ suất sinh đặc
trưng theo tuổi được cộng dồn
từ x = 15 tới x = 49.
Trong thực tế, tổng tỷ suất
sinh được tính bằng phương
pháp rút gọn hơn. Trong
trường hợp tỷ suất sinh đặc
trưng được tính cho nhóm 5 độ
tuổi thì
chỉ số (i) biểu thị các khoảng cách 5 tuổi,
như: 15 - 19, 20 - 24,..., 45 - 49.
Công
thức tính theo nhóm 5 độ tuổi:
![]()
Trong
đó:
TFR: Tổng tỷ
suất sinh;
Bi: Số trẻ sinh ra sống
trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu của những bà
mẹ thuộc nhóm tuổi (i);
i: Nhóm tuổi thứ
i;
Wi: Số
phụ nữ thuộc nhóm tuổi (i) có
đến thời điểm nghiên cứu.
Hệ
số 5 trong công thức trên nhằm áp dụng cho
tỷ suất bình quân của nhóm 5 độ tuổi
liên tiếp sao cho tổng tỷ suất sinh sẽ
tương xứng với tổng các tỷ suất
đặc trưng từng độ tuổi nêu trong
công thức trên.
Tỷ suất chết thô
Tỷ
suất chết thô cho biết cứ 1000 dân, có bao
nhiêu người bị chết trong thời kỳ
nghiên cứu.
Công
thức tính:
|
CDR (‰) |
= |
D |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Trong
đó:
CDR: Tỷ suất
chết thô;
D: Tổng số
người chết trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu;
Ptb: Dân
số trung b́nh trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Tỷ suất chết của
trẻ em dưới 1 tuổi là số đo mức
độ chết của trẻ em trong năm đầu
tiên của cuộc sống, được định
nghĩa là số trẻ em dưới 1 tuổi chết
tính b́nh quân trên 1000 trẻ em sinh ra sống trong thời kỳ
nghiên cứu.
![]()
Trong
đó:
IMR: Tỷ suất
chết của trẻ em dưới 1 tuổi;
D0: Số
trẻ em chết ở độ tuổi dưới 1 tuổi
trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu;
B: Tổng số
trường hợp sinh ra sống trong thời kỳ nghiên
cứu.
Tỷ suất
chết của trẻ em dưới 5 tuổi là số đo mức độ chết của
trẻ em trong 5 năm đầu tiên của cuộc sống,
được định nghĩa là số trẻ em
dưới 5 tuổi chết tính b́nh quân trên 1000 trẻ em
sinh ra sống trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
![]()
Trong
đó:
U5MR: Tỷ suất
chết của trẻ em dưới 5 tuổi;
5D0:
Số trẻ em chết ở độ tuổi dưới
5 tuổi trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu;
B: Tổng số
trường hợp sinh ra sống trong thời kỳ nghiên
cứu.
Tỷ lệ tăng dân số
tự nhiên là mức chênh lệch giữa số
sinh và số chết so với dân số trong thời kỳ
nghiên cứu. Tỷ lệ tăng dân số tự nhiên
được biểu thị bằng tỷ
lệ phần trăm hoặc phần ngh́n.
Công thức tính:
|
NIR |
= |
B - D |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Trong đó:
NIR:
Tỷ lệ tăng dân số tự nhiên;
B:
Tổng số sinh trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu;
D:
Tổng số chết trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu;
Ptb:
Dân số trung b́nh trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Tỷ
lệ tăng dân số chung
(gọi tắt là tỷ lệ tăng dân số) phản ánh mức
tăng/giảm dân số trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu do
tăng tự nhiên và di cư thuần. Tỷ lệ tăng dân số chung được biểu thị
bằng tỷ lệ phần trăm hoặc phần
ngh́n.
Tỷ
suất nhập cư phản ánh số người từ
đơn vị lănh thổ khác (nơi xuất cư) nhập
cư đến một đơn vị lănh thổ trong kỳ
nghiên cứu tính b́nh quân trên 1000 dân của đơn vị
lănh thổ đó (nơi nhập cư).
Công
thức tính:
|
IR (‰) |
= |
I |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Trong đó:
IR: Tỷ suất
nhập cư;
I: Số
người nhập cư trong 12 tháng trước thời
điểm nghiên cứu;
Ptb: Dân
số trung b́nh thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Tỷ suất
xuất cư phản
ánh số người xuất cư của một
đơn vị lãnh thổ trong thời kỳ nghiên cứu
tính b́nh quân trên 1000 dân của đơn vị lãnh thổ
đó.
Công
thức tính:
|
OR (‰) |
= |
O |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Trong đó:
OR: Tỷ suất
xuất cư;
O: Số
người xuất cư trong 12 tháng trước thời
điểm nghiên cứu;
Ptb: Dân
số trung b́nh thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Tỷ suất di cư thuần
phản ánh t́nh trạng nhập cư của dân số vào một
đơn vị lănh thổ và t́nh trạng xuất cư của
dân số ra khỏi đơn vị lănh thổ trong thời
kỳ nghiên cứu. Tỷ suất di cư thuần
được tính bằng hiệu số giữa người
nhập cư và người xuất cư của một
đơn vị lănh thổ trong kỳ nghiên cứu tính b́nh
quân trên 1000 dân của đơn vị lănh thổ đó.
Công thức tính:
|
NR (‰) |
= |
I - O |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Trong
đó:
NR: Tỷ suất
di cư thuần;
I: Số
người nhập cư trong 12 tháng trước thời
điểm nghiên cứu;
O: Số
người xuất cư trong 12 tháng trước thời
điểm nghiên cứu;
Ptb: Dân
số trung b́nh thời kỳ nghiên cứu.
Hoặc: NR = IR - OR
Trong đó:
NR: Tỷ suất
di cư thuần;
IR: Tỷ suất
nhập cư;
OR: Tỷ suất
xuất cư.
Tuổi thọ trung b́nh
tính từ lúc sinh phản ánh triển
vọng một người mới sinh có thể
sống được bao nhiêu năm nếu như mô
hình chết hiện tại được tiếp
tục duy tŕ, đây là chỉ tiêu thống kê chủ
yếu của Bảng sống.
![]()
Trong
đó:
e0: Tuổi
thọ trung bình tính từ lúc sinh
(đơn vị tính: năm);
T0: Tổng số năm của
những người mới sinh trong Bảng
sống sẽ tiếp tục sống được;
l0: Số người
sống đến độ tuổi 0 của Bảng
sống (tập hợp sinh ra sống ban đầu
được quan sát);
Tuổi
thọ trung bình tính từ lúc sinh là
một trong những chỉ tiêu tổng hợp
được tính từ Bảng sống.
Bảng
sống là bảng thống kê bao gồm những
chỉ tiêu biểu thị khả năng sống của
dân số khi chuyển từ độ tuổi này
sang độ tuổi khác và mức độ
chết của dân số ở các độ tuổi
khác nhau. Bảng sống cho biết từ một
tập hợp sinh ban đầu (cùng một
đoàn hệ), sẽ có bao nhiêu người
sống được đến 1 tuổi,
2 tuổi,..., 100 tuổi,…; trong số đó có bao
nhiêu người ở mỗi độ tuổi nhất
định bị chết và không sống
được đến độ tuổi sau;
những người đã đạt
được một độ tuổi nhất
định sẽ có xác suất sống và
xác suất chết như thế nào; tuổi
thọ trung bình trong tương lai là bao nhiêu.
Tỷ lệ dân số từ
15 tuổi trở lên biết chữ phản
ánh tŕnh độ về biết đọc, biết
viết của dân số, phục vụ việc
đánh giá trình độ phát triển của
một quốc gia, một vùng hay một địa
phương.
Chỉ
tiêu này được tính là tỷ lệ giữa
số người từ 15 tuổi trở lên
tại thời điểm nhất định biết
chữ (có thể đọc, viết và
hiểu được một câu đơn giản
bằng chữ quốc ngữ, chữ dân
tộc hoặc chữ nước ngoài) so với
tổng dân số từ 15 tuổi trở lên tại
thời điểm đó.
|
Tỷ lệ dân số từ 15 tuổi |
= |
Số người từ 15 tuổi
trở lên biết chữ |
× 100 |
|
Tổng số dân số từ 15 tuổi trở
lên |
Số
cuộc kết hôn: Kết
hôn là việc nam và nữ xác lập quan hệ vợ chồng
với nhau theo quy định của Luật Hộ tịch
và Luật Hôn nhân và Gia đ́nh về điều kiện kết
hôn và đăng kư kết hôn.
Nam, nữ kết hôn với nhau phải
tuân theo các điều kiện sau đây:
a) Nam từ đủ 20 tuổi trở
lên, nữ từ đủ 18 tuổi trở lên;
b) Việc kết hôn do nam và nữ tự
nguyện quyết định;
c) Không bị mất năng lực hành vi
dân sự;
d) Việc kết hôn không thuộc một
trong các trường hợp cấm kết hôn theo quy định
của Luật Hôn nhân và Gia đ́nh.
Tuổi
kết hôn trung b́nh lần đầu: Tuổi kết hôn trung b́nh lần đầu
của dân số là số năm trung b́nh mà mỗi người
sẽ sống độc thân trong suốt cuộc đời
của ḿnh, nếu như thế hệ này có tỷ trọng
độc thân theo độ tuổi như tỷ trọng
độc thân thu được tại thời điểm
điều tra.
Để có cái nh́n toàn diện về tuổi
bắt đầu cuộc sống có vợ/chồng của
dân số, khi tính tuổi kết hôn trung b́nh lần đầu,
cơ quan thống kê không chỉ xác định những
người có vợ/chồng là những người
đă kết hôn theo quy định của Luật Hôn nhân và
Gia đ́nh mà c̣n xác định cả những người
kết hôn có đủ điều kiện theo quy định
của Luật Hôn nhân và Gia đ́nh nhưng không đăng
kư; kết hôn không đủ điều kiện theo quy
định của Luật Hôn nhân và Gia đ́nh; tảo hôn;
sống với nhau như vợ chồng.
Công
thức tính:
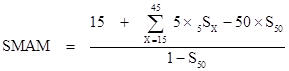
Trong
đó:
SMAM: Tuổi kết
hôn trung b́nh lần đầu.
5SX:
Tỷ trọng độc thân trong nhóm 5 độ tuổi:
x -> x+5.
S50: Tỷ trọng độc
thân chính xác ở độ tuổi 50 và S50
được tính bằng cách lấy giá trị trung b́nh của
5S45 và 5S50.
Số vụ ly hôn là số vụ, việc đă
được Ṭa án cấp sơ thẩm giải quyết
cho các cặp vợ chồng được ly hôn bằng bản
án, quyết định theo Luật Hôn nhân và Gia đ́nh.
Để bảo đảm ý
nghĩa phân tích thống kê, chỉ tiêu này
được tính thông qua tỷ suất ly hôn.
Công thức tính:
|
Tỷ suất ly hôn |
= |
Số vụ, việc ly hôn |
× 1000 |
|
Dân số trung bình |
Tuổi ly hôn trung b́nh
Tuổi
ly hôn trung b́nh của dân số là trung b́nh cộng tuổi của
tất cả các cá nhân có xảy ra sự kiện ly hôn trong
kỳ báo cáo.
Công
thức tính:
|
Tuổi ly hôn |
= |
Tổng số tuổi của những người
ly hôn |
|
Tổng số người ly hôn |
Tỷ lệ trẻ em
dưới 05 tuổi đă được đăng kư
khai sinh
Trẻ
em dưới 05 tuổi đă được đăng kư
khai sinh là số trẻ em dưới 05 tuổi tính từ
ngày sinh, được đăng kư khai sinh và cấp Giấy
khai sinh theo quy định của Luật Hộ tịch.
Tỷ
lệ trẻ em dưới 05 tuổi đă được
đăng kư khai sinh là tỷ lệ phần trăm giữa
số trẻ em dưới 05 tuổi đă được
đăng kư khai sinh so với tổng số trẻ em
dưới 05 tuổi trong kỳ báo cáo.
Công
thức tính:
|
|
|
Số trẻ
em dưới 05 tuổi |
|
|
Số trẻ
em dưới 05 tuổi |
Số
trường hợp tử vong được đăng
kư khai tử: Số
trường hợp tử vong được đăng
kư khai tử là số trường hợp chết
được đăng kư khai tử trong kỳ nghiên cứu.
Số trường hợp tử vong được
đăng kư khai tử gồm cả các trường hợp
tuyên bố chết theo bản án/quyết định của
ṭa án và đă được ghi vào sổ việc thay đổi
hộ tịch theo quy định tại Luật Hộ tịch,
đăng kư khai tử đúng hạn và đăng kư khai tử
quá hạn.
LAO
ĐỘNG VÀ VIỆC LÀM
Lực lượng lao động (hay c̣n gọi là dân số hoạt động
kinh tế hiện tại) gồm những người từ
đủ 15 tuổi trở lên có việc làm (đang làm việc)
hoặc thất nghiệp trong thời kỳ tham chiếu
(7 ngày trước thời điểm quan sát).
Số
lao động đang làm việc (có việc làm) trong nền
kinh tế: Lao động
đang làm việc (có việc làm) là tất cả những
người từ đủ 15 tuổi trở lên, trong thời
gian tham chiếu có làm bất cứ việc ǵ (không bị
pháp luật cấm) từ 01 giờ trở lên để tạo
ra các sản phẩm hàng hóa hoặc cung cấp các dịch vụ
nhằm mục đích được nhận tiền công,
tiền lương hoặc để thu lợi nhuận.
Lao động đang làm việc (có việc làm) không bao gồm
những người làm các công việc tự sản tự
tiêu trong lĩnh vực nông, lâm nghiệp và thủy sản,
tức là những người làm việc để tạo
ra sản phẩm mà mục đích chủ yếu là để
ḿnh hoặc gia đ́nh ḿnh sử dụng.
Người đang làm việc (có việc
làm) gồm cả những người không làm việc trong
tuần nghiên cứu nhưng đang có một công việc
(không bao gồm công việc tự sản tự tiêu) và vẫn
gắn bó chặt chẽ với công việc đó (vẫn
được trả lương/công trong thời gian không
làm việc hoặc chắc chắn sẽ quay trở lại
làm sau thời gian không quá 01 tháng).
Ngoài ra, những trường hợp cụ
thể sau đây cũng được coi là người
đang làm việc (có việc làm):
a) Người đang tham gia các hoạt
động tập huấn, đào tạo hoặc các hoạt
động nâng cao kỹ năng do yêu cầu của công việc;
b) Người học việc, tập sự
(kể cả bác sỹ thực tập) làm việc và có nhận
được tiền lương, tiền công;
c) Sinh viên/học sinh/người nghỉ
hưu trong thời kỳ tham chiếu có làm một công việc
(không bao gồm công việc tự sản tự tiêu) từ
01 giờ trở lên để tạo thu nhập;
d) Người đang t́m kiếm việc
làm/người đăng kư hoặc người nhận bảo
hiểm thất nghiệp nhưng trong thời kỳ tham
chiếu có làm một công việc (không bao gồm công việc
tự sản tự tiêu) từ 01 giờ trở lên để
tạo thu nhập;
đ) Lao động gia đ́nh: Những
người làm việc v́ mục đích để nhận
tiền công, tiền lương hoặc lợi nhuận
nhưng các khoản tiền lương, tiền công và lợi
nhuận đó có thể không trả trực tiếp mà
được tích lũy vào thu nhập chung của gia
đ́nh.
Tỷ
lệ lao động đang làm việc so với tổng
dân số là tỷ lệ
phần trăm tổng số người đang làm việc
chiếm trong tổng dân số.
|
Tỷ lệ
lao động đang làm việc |
= |
Số người đang làm việc |
× 100 |
|
Tổng dân số |
Tỷ lệ lao động
đă qua đào tạo là chỉ tiêu phản
ánh tỷ lệ so sánh số lao động đă qua đào
tạo có bằng cấp, chứng chỉ với tổng số
lực lượng lao động trong kỳ.
|
Tỷ lệ lao động |
= |
Lao động đă qua đào tạo |
× 100 |
|
Tổng lực lượng lao động |
Lao
động đă qua đào tạo có bằng cấp, chứng
chỉ bao gồm những người thỏa măn cả
hai điều kiện sau đây:
-
Đang làm việc trong nền kinh tế hoặc thất
nghiệp;
-
Đă được đào tạo ở một trường
hay một cơ sở đào tạo chuyên môn, kỹ thuật,
nghiệp vụ thuộc Hệ thống giáo dục quốc
dân từ 3 tháng trở lên, đă tốt nghiệp,
được cấp bằng/chứng chỉ chứng nhận
đă đạt một tŕnh độ chuyên môn, kỹ thuật,
nghiệp vụ nhất định, bao gồm: sơ cấp nghề, trung cấp
nghề, cao đẳng nghề, trung cấp chuyên nghiệp,
cao đẳng chuyên nghiệp, đại học và trên
đại học (thạc sỹ, tiến sỹ, tiến
sỹ khoa học).
Tỷ
lệ thất nghiệp
Số người
thất nghiệp là
người từ đủ 15 tuổi trở lên mà trong thời
kỳ tham chiếu có đầy đủ cả 03 yếu
tố: Hiện không làm việc, đang t́m kiếm việc
làm và sẵn sàng làm việc.
Người thất nghiệp c̣n là những
người hiện không có việc làm và sẵn sàng làm việc
nhưng trong thời kỳ tham chiếu không đi t́m việc
do đă chắc chắn có một công việc hoặc một
hoạt động sản xuất kinh doanh để bắt
đầu sau thời kỳ tham chiếu.
Tỷ
lệ thất nghiệp là tỷ lệ
phần trăm giữa số người thất nghiệp
so với lực lượng lao động.
Công
thức tính:
|
Tỷ lệ thất nghiệp |
= |
Số người thất nghiệp |
× 100 |
|
Lực lượng lao động |
Tỷ lệ thiếu việc làm
Số
người thiếu việc làm gồm những
người có việc làm trong thời gian tham chiếu (07
ngày trước thời điểm quan sát) thoả măn cả
03 tiêu chuẩn sau đây:
a) Thực tế họ
đă làm tất cả các công việc dưới ngưỡng
thời gian 35 giờ.
b) Mong muốn làm việc
thêm giờ, nghĩa là: Muốn làm thêm một (hoặc một
số) công việc để tăng thêm giờ; muốn
thay thế một trong số (các) công việc đang làm bằng
một công việc khác để có thể tăng thêm giờ;
muốn tăng thêm giờ của một trong các công việc
đang làm hoặc kết hợp 3 loại mong muốn trên.
c) Sẵn sàng làm việc
thêm giờ, nghĩa là: Trong thời gian tới (ví dụ
trong tuần tới) nếu có cơ hội việc làm th́ họ
sẵn sàng làm thêm giờ.
Tỷ
lệ thiếu việc làm là chỉ tiêu phản
ánh tỷ lệ so sánh số người thiếu việc làm
với tổng số người đang làm việc trong nền
kinh tế.
Công thức tính:
|
Tỷ lệ thiếu việc làm |
= |
Số người thiếu việc làm |
× 100 |
|
Tổng số người đang làm việc |
Tỷ lệ lao động
có việc làm phi chính thức
Lao động có việc làm phi chính thức là
những người có việc làm thuộc một trong
năm nhóm sau: (i) Lao động gia đ́nh không được
hưởng lương, hưởng công; (ii) Người
chủ của cơ sở, lao động tự làm trong
khu vực phi chính thức; (iii) Người làm công hưởng
lương không được kư hợp đồng lao
động hoặc được kư hợp đồng
lao động nhưng không được cơ sở tuyển
dụng đóng bảo hiểm xă hội theo h́nh thức bắt
buộc; (iv) Xă viên hợp tác xă không đóng bảo hiểm
xă hội bắt buộc; (v) Lao động tự làm hoặc
lao động làm công hưởng lương trong các hộ
gia đ́nh hoặc hộ nông, lâm nghiệp và thủy sản.
Lao động trong khu vực hộ nông, lâm
nghiệp và thủy sản.
Tỷ
lệ lao động có việc làm phi chính thức là tỷ
lệ phần trăm giữa số người có việc
làm phi chính thức so với tổng số lao động
có việc làm.
Công
thức tính:
|
Tỷ lệ lao động có việc làm |
|
Số lao động có việc làm |
|
|
Số lao động có việc làm |
Năng suất lao động
Năng suất lao động phản
ánh hiệu suất làm việc của lao động,
thường đo bằng tổng sản phẩm trong
nước tính b́nh quân một lao động trong thời kỳ
tham chiếu.
Công thức tính:
|
Năng
suất lao động |
= |
Tổng
sản phẩm trong nước (GDP) |
|
Tổng
số người làm việc b́nh quân |
Thu
nhập b́nh quân một lao động đang làm việc
Thu nhập của lao
động đang làm việc bao gồm những khoản
thu nhập sau:
- Thu nhập từ tiền công, tiền
lương và các khoản thu nhập khác có tính chất
như lương, gồm: Tiền làm thêm, tiền thưởng,
tiền phụ cấp,… của những người lao
động làm công hưởng lương trong nền kinh
tế. Các khoản thu nhập này có thể bằng tiền
hoặc hiện vật.
- Thu nhập từ các hoạt động
sản xuất kinh doanh, gồm: Thu lợi từ các hoạt
động sản xuất nông nghiệp để bán sản
phẩm, lợi nhuận từ việc kinh doanh hàng hóa, dịch
vụ,... không bao gồm những khoản thu nhập từ
lăi suất cho vay hay lợi tức được trả
mà không liên quan đến công việc đang làm.
Thu nhập b́nh quân một lao động
đang làm việc là tổng thu nhập của tất cả
lao động đang làm việc so với tổng số
lao động đang làm việc.
Công
thức tính:
|
|
|
Tổng thu nhập của tất cả |
|
Tổng số lao động có việc làm |
EXPLANATION OF TERMINOLOGY, CONTENT
AND METHODOLOGY OF SOME STATISTICAL INDICATORS ON POPULATION AND LABOUR
POPULATION
Population
is the group of people living in a country, region, economic geographical zone
or an administrative unit.
In
statistics, population is collected in line with the definition of actual
permanent resident of a household, who actually stays and eats at the household
for 6 months or more by the time-point of the enumeration, newborns prior the
time-point of the enumeration and people who have recently moved to this
household will live permanently at the household regardless of with or whithout
permanent residence at the residing commune, ward, town and those who have been
temporarily absent. The actual permanent residents in the household include:
-
Persons who eat, live permanently in
the household for 6 months or over by time-point of the enumeration.
-
Persons who have recently moved to the household less than 6 months but are
identified to stay and eat permanently at the household and newborns preceding
the survey time-point, irrespective of whether they were legally certificated
or not for their movement.
-
Persons who lived permanently in the household but have been currently absent
for less than 6 months by the time of enumeration; who have been working or
studying domestically within 6 months; who have been to their relative' houses
for a visit, on summer vacations, holidays, traveling, firmly come back to the
household; who have been on business trips, maritime fishing, ocean ships,
merchants; who have been permitted by authorities to go overseas for working,
business, study, medical treatment, and tourism for an assigned duration of
time by the time of enumeration; who have had inpatient treatment at medical
establishments; who have been detained by the military or police.
Average population
Average
population is mean population for a period.
Formula:
- If data is available
at two time points (base and end of the short term, usually a year), then use
the following formula:
|
Ptb |
= |
P0 + P1 |
|
2 |
Where:
Ptb: Average population;
P0: Population at the
base period;
P1: Population at the
ending period.
- If data is available
at times evenly, then use the formula:
|
|
|
P0 |
+ P1 |
+ .... |
+ Pn-1 + |
Pn |
|
2 |
2 |
|||||
|
n |
||||||
Where:
Ptb: Average population;
P0,1,...,n: Population
at time points of 0, 1,...,;
n: Number of equal time points.
- If data are available
at times unequal spaces, using the formula:
|
Ptb |
= |
Ptb1t1
+ Ptb2t2 + .... + Ptbntn |
|
∑ti |
Where:
Ptb:
Average population;
Ptb1: Average population
of the first duration;
Ptb2: Average population
of the second duration;
Ptbn: Average population
of the nth duration;
ti: Length of the ith
duration.
Urban
population is the population of the territorial units which is
designated as urban areas by the State (wards, town).
Rural
population is the population of the territorial units which is
designated as rural areas by the State (communes).
Population density
is the average population per square kilometer of the territory.
Population
density is calculated by dividing the population (at time point or average
population) of a certain residential area to the area of that territory.
Population density can be calculated for the entire
country or region (rural, urban, socio-economic region), for each province,
district, commune, etc.
in order to reflect the population distribution by geography at a given time.
Formula:
|
Populationn density |
= |
Population |
|
Territory area |
Number of households
Household
is a social unit, comprising either one person living alone or a group of
people living in the same dwelling and sharing meals together. For households
with 2 persons or over, its members may or may not share a common budget; or be
related by blood or not; or in combination of both.
Sex ratio of the population
reflects number of males per 100 females. Sex ratio of the population is
determined by the following formula:
|
Sex
ratio |
= |
Total
of males |
×
100 |
|
Total
of females |
Crude birth rate
Crude
birth rate indicates that for every 1,000 people, how many live births are in
the reference period.
Formula:
|
CBR (‰) |
= |
B |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Where:
CBR: Crude birth rate;
B: Total live births in
the reference period (total of children were born alive in the reference
period);
Ptb:
Population up to the reference time-point.
Total
fertility rate (TFR)
Total
fertility rate reflects the average number of live births that would be born
per woman during the childbirth period if the woman passes age-specific
fertility rates observed in a given reference period during the reproductive
period.
Formula by age group:
![]()
Where:
TFR: Total fertility
rate (children per woman);
Bx: Number
of live births registered in the year of women aged (x);
![]() :
One-year age interval;
:
One-year age interval;
Wx: Number
of women aged (x) at the calculation mid-year.
Age
specific fertility rates are accumulated from x = 15 to x = 49.
In fact, the total fertility rate is calculated by the
abridged method. In case the age specific fertility rates
are calculated for 5-year age groups, index of (i) represents the 5-years
interval of age, such as 15-19, 20-24, ..., 45-49.
Formula
by 5-year interval of age:
![]()
Where:
TFR: Total fertility
rate;
Bi: Number of live births in the
reference period of women in the age group (i);
i: ith age
group;
Wi: Number of women of
the ith age group up to the reference time-point.
The
coefficient of 5 in the above formula is applied for the average rate of
consecutive 5-year age groups so that the TFR will be commensurate with the
age-specific fertility rates described in this formula.
Crude death rate
Crude
death rate indicates that for every 1,000 people, how many deaths are in the
reference period.
Formula:
|
CDR (‰) |
= |
D |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Where:
CDR: Crude death rate;
D: Total of deaths in
the reference period;
Ptb:
Population up to the reference time-point.
Infant mortality rate is
the measure of the mortality level of children in the first year of life. This
rate is defined as the number of children under one year of age per 1,000 live
births in the reference period on average.
![]()
Where:
IMR: Infant mortality
rate;
D0: Number of deaths of children under one
year of age in the reference period;
B: Total of live births
in the reference period.
Under five mortality rate
is the measure of mortality level of children in the first five years of life.
This rate is defined as the number of deaths of children under age 5 per 1,000
live births in the reference period on average.
![]()
Where:
U5MR: Under five
mortality rate;
5D0:
Number of deaths under age 5 in the reference period;
B: Total of live births
in the reference period.
Natural
increase rate of population is the difference between
number of live births and number of deaths to the population in the reference
period. The natural increase rate of population is expressed as a percentage or
per mille.
Formula:
|
NIR |
= |
B - D |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Where:
NIR: Natural Increase
Rate of population;
B: Total number of live
births in the reference period;
D: Total number of
deaths in the reference period;
Ptb: Average
population in the reference period.
Growth rate of
population (growth rate) reflects the
increase/decrease of the population in reference period due to natural increase
and net-migration. Growth rate of population is expressed as a percentage or
per mille.
In-migration rate
are the number of people from different territorial units (out-migration place)
in-migrate to a territorial unit in the reference period (usually a calendar
year) on an average per 1,000 population of that territorial unit (in-migration
place).
Formula:
|
IR (‰) |
= |
I |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Where:
IR: In-migration rate;
I: Number of
in-migrants in 12 months prior to the reference period;
Ptb: Average
population in the reference period.
Out-migration
rate reflects the number out-migrants
of a territorial unit in the reference period on average per 1,000 population
of that territorial unit.
Formula:
|
OR (‰) |
= |
O |
× 1000 |
|
Ptb |
Where:
OR:
Out-migration rate;
O: Number of
out-migrants in 12 months prior to the reference period;
Ptb:
Population up to the reference time-point.
Net-migration rate
reflects the status of in-migration and out-migration of population into/out
from a territorial unit in the reference period. It is the difference between
number of in-migrants and number of out-migrants of a territorial unit on
average per 1,000 population of that territorial unit.
Formula:
|
NR (‰) |
= |
I - O |
× |
1000 |
|
Ptb |
Where:
NR: Net-migration rate;
I: Number of
in-migrants in 12 months prior to the reference period;
O: Number of out-migrants
in 12 months prior to the reference period;
Ptb:
Population up to the reference time-point.
Or:
NR =
IR - OR
Where:
NR: Net-migration rate;
IR: In-migration rate;
OR: Out-migration rate.
Life expectancy
at birth reflects the prospect of a newborn could live for how many years if
the current mortality model is maintained, this is the key statistical
indicator of the Life table.
![]()
Where:
e0: Life
expectancy at birth (unit: year);
T0: Total number of years of the newborns in
the Life table who will continue to live;
l0: Number of persons who live to the age of
0 of the Life table (the set of original newborns is observed).
Life
expectancy at birth is one of the integrated indicators calculated from the
Life table.
The Life table is a statistical table that includes the
indicators showing the viability of population moving from one age to the next
and the mortality of the population at different ages. The Life table shows
that from an initial set of the births (on the same cohort), there will be how
many persons who will live to 1 year, 2 years,..., 100 years,...; among them,
there are how many persons at each of the certain ages who will be dead before
the following age; those persons who have reached a certain age will have what
probability of survival and death; how long is the life expectancy in the
future.
Rate
of literate population aged 15 and over reflects the ability of reading and writing of the population, serves to
assess the development level of a country, region or locality.
This
indicator is calculated as the rate between the number of persons aged 15 years
and over at specific time who are literate (able to read, write and understand
a simple sentence in the national language, ethnic or foreign language) and the
total population aged 15 years and over at that time.
|
Rate of literate population |
= |
Literate population |
× 100 |
|
Total population |
Number of marriages: Marriage means a marriage between a man and a woman
according to the provisions of the Marriage and Family Law regarding conditions
of marriage and marriage registration.
Men and women
getting married must comply with the following conditions:
a) Man is from
20 years of age or older, woman is from 18 years old
or older;
b) The
marriage is voluntarily decided by men and women;
c) Do not lose
civil act capacity;
d) Marriage
does not fall into one of the circumstances where marriage is prohibited under
the Law on Marriage and Family.
Singulate mean age at marriage (SMAM):
Singulate mean age at marriage of the population is the average number of years
of single person in their whole life, if this generation has proportion of
single age as the proportion of single person collected at the survey time
point.
In
order to have an overall view on the age of starting a married life of the
population, when calculating the singulate mean age at marriage, the
statistical agency not only identifies married persons who are married as
stipulated by the Law on Marriage and Family but also identifies married
persons who satisfy conditions as stipulated by the Law on Marriage and Family
but have not been certificated; those who are married but do not satisfy
conditions as stipulated by the Law on Marriage and Family; those who are child
mariage; and those who cohabit with the opposite sex.
Formula:
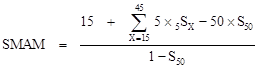
Where:
SMAM: Singulate mean
age at marriage.
5SX:
Proportion of single age in 5-year interval of age: x -> x+5.
S50: Proportion of single age at the age of
50 years old and S50 is calculated by average value of 5S45
và 5S50.
Number
of divorce cases is the
number of cases which have been addressed for couples to get divorce by the
Court of first instance under the Law on Marriage and Family.
To ensure statistical analysis meaning, this indicator
is calculated through the divorce proportion.
Formula:
|
Proportion of divorce |
= |
The number of divorce cases |
× 1000 |
|
Average population |
Average age of divorce
The
population’s average age of divorce is the arithmetic mean age of all individuals
whose divorce events occurred during the reporting period.
Formula:
|
Average age |
= |
Total age of divorced persons |
|
Total number of divorced persons |
The rate of under-5 children
registered with birth certificate
Under-5
children registered with birth certificate are the number of children under 5
years old counted at their date of birth certificated and granted with birth
certificate in accordance with the Law on Civil Status.
The
rate of under-5 children registered with birth certificate is the percentage of
the number of under-5 children registered with birth certificate to the total
number of under-5 children in the reporting period.
Formula:
|
The rate of under-5 |
|
Number of under-5 children registered with birth certificate |
|
|
Number of under-5 children |
Number
of deaths registered with death certificate: The number of deaths registered with death certificate
is the number of deaths registered with death certificate in the reference period.
The number of deaths registered with death certificate comprises those who were
declared to be dead in accordance with the court judgments/decisions and
recorded in the register of civil status change in line with the Law on Civil
Status, and those who are death certificate registration on time and overdue.
LABOR AND EMPLOYMENT
Labor force
(also known as current economically active population) comprises of all persons
aged 15 years and over who are the employed (working) or the unemployed during
the reference period (7 days prior to the time of observation).
Number of working (employed) labors
in the economy: Working (employed) labors consist
of all persons aged 15 years and over who did any job during the reference
period (not prohibited by law) for at least one hour to create goods or provide
services for pay or profit. Working (employed) labors do not include those who
are self-employed in the agricultural, forestry and fishery sector, i.e. those
who work to produce own-use products for their my family and themselves.
Working
(employed) persons comprise those who do not work during the research week but
have a job (excluding self-employed job) and work on it after days-off (they
are still eligible for salary/wage in days-off or going to continue working
after less than one month days-off).
In
addition, the following specific cases are also considered as working
(employed) persons:
a)
People are participating in skill training or improvement activities as
required from their jobs;
b) People work as apprentices, internship (even doctor
internship) for pay;
c)
Students/pupils/pensioners have a job in the reference period (excluding
self-employed job) for at least one hour for income;
d)
Those who are job-seekers/job-registrants or unemployment insurance claimers
but have a job in the reference period (excluding self-employed work) for at
least one hour for income;
đ)
Family workers: Those who work for pay or profits but such payments and profits
are not be paid directly to them but accumulated in general income of their
family.
Employment to population ratio is the percentage of total employed persons to
total population.
|
Employment to |
= |
Employed population |
× 100 |
|
Total population |
Rate of trained labour
force is the indicator reflecting
the comparable rate of trained labour force to total number of persons in
labour force in
the period.
|
Rate of trained |
= |
Number of trained in labour force |
× 100 |
|
Total number of labour force |
Number
of trained labour includes those who satisfy both of the following conditions:
-
Be employed in the economy or unemployment;
- Have been trained in a training or an establishment
whose responsibility is training in professional, technical knowledge under the
National Education System for 3
months and more, have been graduated or granted the degree/certificate
including: short-term training, vocational secondary school, vocational
college, professional secondary school, college, university and post-graduate
(master, doctor, and science doctorate).
Unemployment
rate
The number of
unemployed persons is persons aged 15 years and over,
met the following factors in the reference period: (i) currently not working;
(ii) seeking employment; (iii) ready to work.
Unemployed
population also consists of those persons who are currently unemployed and
ready to work but do not seek employment in the reference period, due to have
been able to get work or business/productive activities to start after the
reference period.
Unemployment rate
expressing the rate between the number of unemployed persons and the labor
force.
|
Unemployment rate |
= |
Number of unemployed persons |
×
100 |
|
Labour force |
Underemployment rate
The
number of underemployed persons comprise those who are
employed during the reference period (07 days prior to the time of observation)
satisfy all three of the following criteria:
a) They actually did all the
work less than 35 hours per week.
b) They desire to work extra
hours, ie: they wish to do one (or more) jobs to increase working hours; wish
to replace one of the current job(s) with another job that can increase working
hours; wish to increase the working hours of one of the current jobs or a
combination of the 3 aforementioned desires.
c) They are willing to work
extra time, ie: in the coming time (for example next week) if there is a job
opportunity, they are willing to work extra hours.
Underemployment rate is the indicator expressing the rate between the
number of underemployed persons and the employed person.
Formula:
|
Underemployment |
= |
Number of under-employed
persons |
× 100 |
|
Total number of employed persons |
Percentage of informal employed
workers
Informal employed workers (informal workers) are those who
have jobs in one of the following five groups: (i) Unpaid family workers; (ii)
Own-account workers, self-employed workers in the informal sector; (iii) Wage
worker who are not allowed to sign a labor contract or are allowed to sign a
labor contract but their compulsory social insurance premiums are not paid by
the recruitment establishment; (iv) Cooperative members who do not pay
compulsory social insurance; (v) Self-employed or wage workers in households or
agriculture, forestry and fishery households.
Workers
in the agriculture, forestry and fishery households.
Informal
employment rate is the ratio of the number of informal employed persons to the
total number of employed persons.
Formula:
|
Informal employment rate |
= |
Number of informal |
× 100 |
|
Total number of |
Labour
productivity is the indicator reflecting the
working performance of labour, usually measured by Gross Domestic Product to a
worker on an average in the reference period, usually a calendar year.
|
Labour productivity |
= |
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) |
|
Average employed population |
Average monthly income per employed
worker
Income
of an employed worker includes the following items:
-
Income from wages, salaries and other incomes of salary-like nature, including: overtime conpensation, bonuses, allowances,
etc. of wage workers in the economy. These incomes can be in cash or in
kind.
-
Income from production and business activities, includes: Profits from
agricultural production activities which sell products, profits from trading in
goods and services,... excluding income from loan interest or income paid that
is not related to the job at hand.
Average
monthly income per employed worker is the total income of all employed workers
to the total number of employed workers.
Formula:
|
Average monthly income |
= |
Total income of all employed workers |
|
Total number of employed workers |